Tips for "Linux on Windows" (Windows Subsystem for Linux, WSL, WSL2)
Previously known as "Bash on Ubuntu on Windows"
- Resources
- FAQ
- From Microsoft Docs
- Additional
- Access Linux Files in Windows
- Access Windows Files in Linux
- Which version of Ubuntu do I get by default?
- What Linux distributions are available?
- How to do release upgrade?
- sudo command takes ages to be executed:
- sudo command reports sudo: unable to resolve host …:
- Startup directory of bash is set to current directory instead of home directory:
- How to change the default user in Bash on Ubuntu on Windows?
- How can I access the Windows filesystem from within the Linux shell?
- How can I access the Linux filesystem from Windows?
- Why newly created file has mode 666 and directory 777?
- How to detect WSL from native Ubuntu/Linux?
- bash.exe fails to start?
- Can "Linux on Windows" / "Bash on Ubuntu on Windows" run in Cygwin?
- Does "Linux on Windows" / "Bash on Ubuntu on Windows" work with ConEmu?
Windows 10 adds an optional feature called Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) since build 14316 which allows you to run Linux distro on Windows. And since build 18917 you can run with WSL2 which increases file system performance and adds full system call compatibility.
For detailed user experience changes between WSL 1 and WSL 2, read this.
Use command winver to check your windows version and build. Here are some related resources and FAQs for WSL 1 and WSL 2.
Resources
Installation Guide
-
WSL 2: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl2-install
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux /all /norestart dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestartRestart.
Update the WSL 2 Linux kernel. https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl2-kernel
wsl --set-default-version 2To update existing distro, run:
wsl --set-version <Distro> 2Install Linux distro at https://aka.ms/wslstore
-
WSL 1: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install-win10
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-LinuxRestart.
Install Linux distro at https://aka.ms/wslstore
Command Reference
Release Info
-
Windows 10 version history - Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Windows_10_version_history#Rings
-
Windows 10 release information
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/release-information/
-
Release Notes for Windows Subsystem for Linux
FAQ
From Microsoft Docs
Additional
Access Linux Files in Windows
-
Via
explorer.exe .in Linux shell; -
Via
\\wsl$in Windows Explorer.
Ref: What’s new for WSL in Windows 10 version 1903? | Windows Command Line
Access Windows Files in Linux
Your Windows files are available at /mnt by default.
You may also edit /etc/wsl.conf in Linux to fine tune the mount:
[automount]
enabled = true
root = /windir/
options = "metadata,umask=22,fmask=11"
mountFsTab = false
Exit Linux shell. Then in Windows command prompt, run wsl --shutdown. Finally, start Linux distro again to make the change in effect.
Your Windows files will be available at /windir as specified in /etc/wsl.conf.
Ref: Manage Linux Distributions | Microsoft Docs
Which version of Ubuntu do I get by default?
If you installed Ubuntu by running bash from a command prompt:
- Ubuntu 16.04.1 LTS (Xenial) for Windows 10 since build 14951 (supported since build 14936);
- Ubuntu 14.04.5 LTS (Trusty) for Windows 10 since build 14316.
Or if you installed it from Windows Store (since build 16215), you get what's offered in the Store:
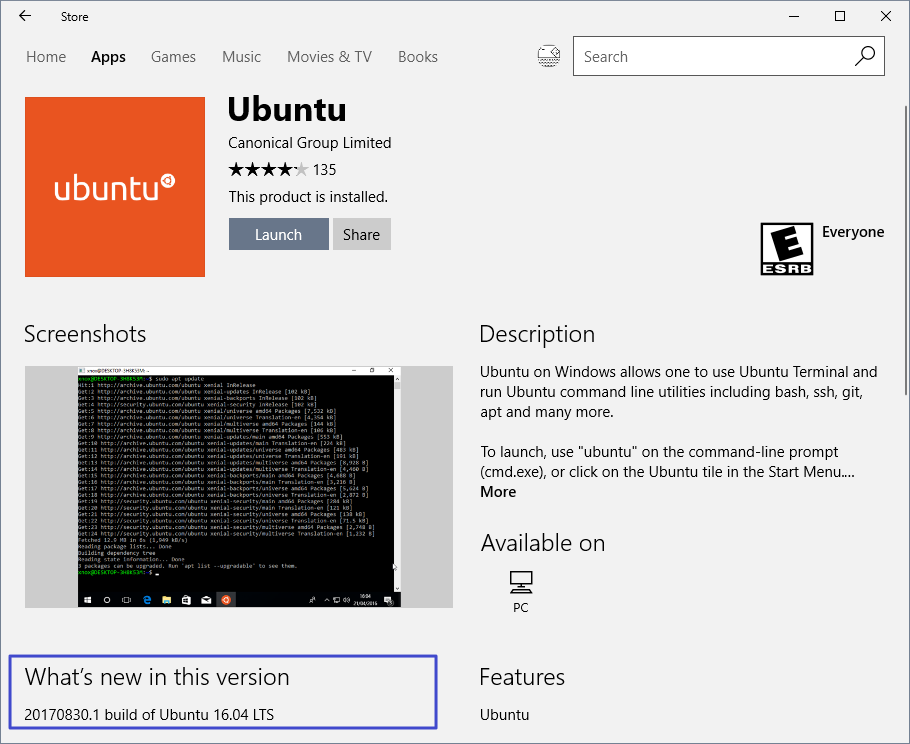
What Linux distributions are available?
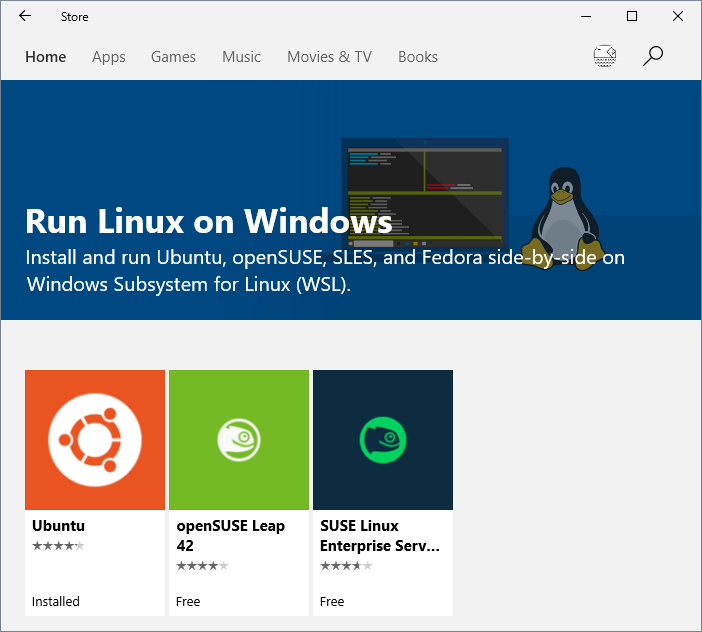
Currently, Ubuntu, openSUSE Leap 42, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 (SLES) are available from the Windows Store for users of Windows 10 build 16215 and later.
Click on direct links above or search linux in Windows Store to access them.
How to do release upgrade?
If you have installed Ubuntu 14.04 LTS (Trusty) and want to upgrade to 16.04 LTS (Xenial). You need to
- Update Windows to build 14936 or later;
- Run
do-release-upgradeinside Bash on Ubuntu on Windows and follow the instructions.
More details on this at Update Linux Subsystem on Windows (Ubuntu) to 16.04 - Super User
sudo command takes ages to be executed:
sudo command reports sudo: unable to resolve host …:
Add your computer name into /etc/hosts file. For example,
127.0.0.1 localhost zzzbuzz
Reference: sudo on Windows 10 Linux subsystem cannot resolve local machine name - Super User
Startup directory of bash is set to current directory instead of home directory:
Use bash ~ to start in home directory, and bash to start in current directory.
How to change the default user in Bash on Ubuntu on Windows?
Run lxrun /setdefaultuser in Windows command line.
How can I access the Windows filesystem from within the Linux shell?
The drives on Windows are mounted under the /mnt folder, e.g. /mnt/c.
How can I access the Linux filesystem from Windows?
The Linux filesystem is located at %LocalAppData%\lxss\rootfs, e.g. C:\Users\Username\AppData\Local\lxss\rootfs. Note that %LocalAppData%\lxss is a hidden system folder.
And user's home folder is stored under %LocalAppData%\lxss\home; root's home folder is located at %LocalAppData%\lxss\root.
However note that:
Please DO NOT manipulate the Linux filesystem from Windows - this may well cause issues and/or corruption.
It's fine to access your Windows filesystem from Linux, but the other way around is not a supported scenario at this time.
The conclusion is, for maximum interoperability, keep files/directories you want to modify in both environments under Windows native filesystem (/mnt/c or C:\, etc.), so that access them in both environments won't cause troubles.
If you do try the unsupported operations, be noted that only copying files out of linux filesystem from Windows works. Pasting/Creating files to Linux filesystem from within Windows won't get recognized by Ubuntu on Windows. Thus, to copy files from Windows environment to Ubuntu on Windows envrionment, do that within Bash on Ubuntu on Windows.
If you do copy files to the filesystem of Ubuntu on Windows within Windows, you may encounter Input/output error when accessing these files from Ubuntu on Windows.
Besides, if you delete files of the Ubuntu filesystem from within Windows, they will still be available to the Ubuntu environment, i.e. these files are just invisible to the Windows environment.
Why newly created file has mode 666 and directory 777?
The umask on Ubuntu is handled by pam_umask by default, but pam is not available on Ubuntu on Windows, effectively making umask be 0000, which causes new files to be in mode 666 and directories in mode 777.
Add the line umask 022 or alike to /etc/profile or ~/.profile to solve this problem.
To fix permission on existing files, you may refer to the following code:
# This removes write permission for group and others on all files under
# user home directory recursively.
chmod -R go-w ~
How to detect WSL from native Ubuntu/Linux?
Search for string Microsoft in /proc/version or /proc/sys/kernel/osrelease.
The content of /proc/version looks like
Linux version 3.4.0-Microsoft ([email protected]) (gcc version 4.7 (GCC) ) #1 SMP PREEMPT Wed Dec 31 14:42:53 PST 2014
The content of /proc/sys/kernel/osrelease looks like 3.4.0-Microsoft.
Example code:
if grep -qsi Microsoft /proc/sys/kernel/osrelease; then
echo "Ubuntu on Windows"
else
echo "Native Linux"
fi
Credits & References:
-
wsl - Detect "Ubuntu on Windows" vs native Ubuntu from bash script - Stack Overflow
- Provide a way to positively detect WSL from an app compiled on Linux. · Issue #423 · Microsoft/BashOnWindows
bash.exe fails to start?
If you run bash.exe and get the following error:
Cannot launch bash because the LX subsystem has an install, uninstall, or servicing operation pending.
Try to stop the LX subsystem service (lxssmanager) (do this as administrator), and run bash.exe again when the service is stopped.
sc stop lxssmanager
Wait for lxssmanager service to stop; check its state with sc query lxssmanager.
When the service is in STOPPED state, run bash.exe again.
Reference: Bug - Cant install and load bash · Issue #591 · Microsoft/BashOnWindows
Can "Linux on Windows" / "Bash on Ubuntu on Windows" run in Cygwin?
No. It exits with error: 0x80070057. (Exit Status: 127)
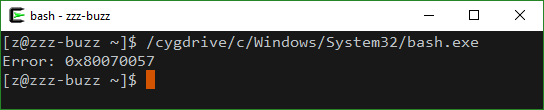
Or fails with Permission denied or even not responding at all in recent builds of Windows.
Does "Linux on Windows" / "Bash on Ubuntu on Windows" work with ConEmu?
Yes.